In the last Gartner Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies, published in August 2023, Generative AI was described as being at the “peak of inflated expectations”. As such, we might have expected the hype to tail off, and disillusion to creep in. However, exactly the opposite happened: The hype surrounding Generative AI continues unabated. In the first months of 2024 Artificial Intelligence has made significant progress. It is moving to become an ever more important part of our daily lives as well as our economy.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in general and Generative AI in particular are not new phenomena. They are well established in business and industry have become central to society in many different ways. What is the difference between AI and Generative AI? And what is so special about them?
From media production to process optimization
Generative AI is a subfield of AI and focusses on creating new, original content, such as texts, images, music and videos. While AI systems are designed to make decisions, recognise patterns, and learn from data, generative AI uses advanced technology, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), to produce creative and realistic content that resembles or imitates content created by humans.
In today’s fast-moving world, where technological development is constantly moving forward, it’s important to understand the current status quo. Working together with the Stuttgart Media University (HDM) and the AI consultancy Perelyn, the BVDW asked decision makers from German companies how far generative AI has already been implemented in their companies. The results give a clear picture: Generative AI is not just an assistive technology, it’s a decisive factor for business success.
Some 96 per cent of German companies say that they can positively influence their business success using generative AI. In addition, 60 per cent of those interviewed say generative AI has a central role in their overall strategy and 95 per cent say that they are open to using generative AI.
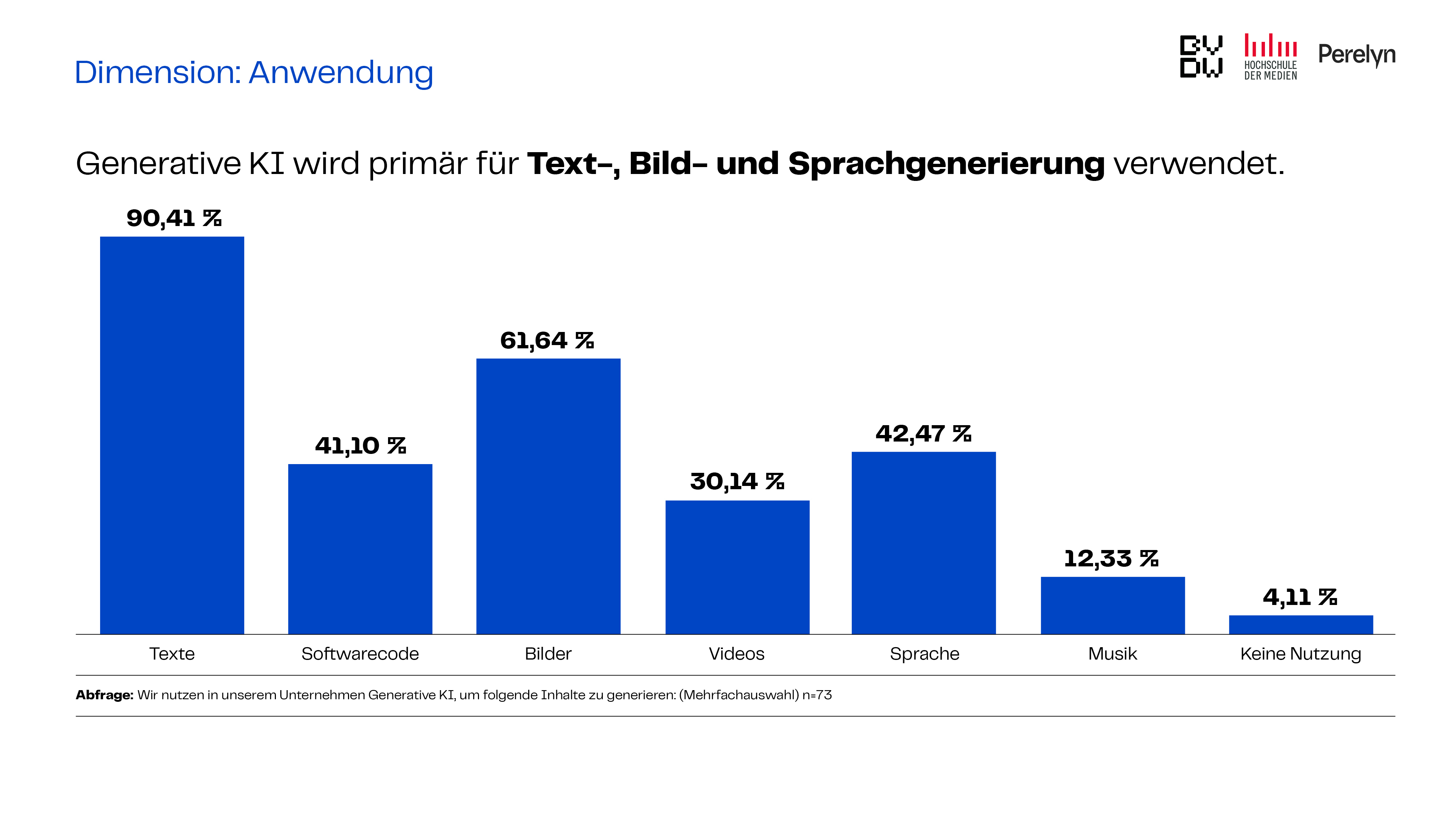
This approach is currently evident in the primary areas of application for generative AI. The results of the study show that 90 per cent of those interviewed use this technology primarily for text generation, 62 per cent to produce images and 43 per cent for speech production. Consequently, we see that content creation and media production are the main current uses of generative AI technologies.
Only 32 per cent of companies use generative AI to optimize business processes and management. This points to a large number of untapped possibilities for using this technology.
Generative AI in process chains: Opportunities to increase efficiency, reduce costs and promote innovation
Using generative AI in process chains provides numerous opportunities to increase efficiency, reduce costs and promote innovation. Let us consider some of the opportunities to increase efficiency.
Generative AI can offer valuable support to optimize process chains, by analysing and evaluating processes and possible options. By simulating different scenarios and evaluating their outcomes, generative AI can assess their efficiency, to help make informed decisions about how to best deploy resources and design processes. This in turn leads to a more efficient use of resources and minimizes waste.
In addition, generative AI can also be deployed to automatically adapt and scale processes for different markets. In dynamic environments, process chains can be set up and managed more flexibly by using generative AI. They react automatically to changes in demand or disruption to processes and make suggestions for adaptations, to guarantee process stability and secure supply chains.
Moreover, using generative AI can bring significant advantages to risk management. The technology’s capacity to be able to simulate future scenarios, and evaluate risks precisely qualifies it as an essential instrument for risk management. Companies are able to identify risks more effectively, and develop well-founded strategies to reduce risks, which in turn brings greater resilience to the process chain.
Such applications show how generative AI could effectively revolutionise process chains in different industries from manufacturing to logistics or from financial services to health services. Here it could be used to unlock potential for efficiency and have a positive effect on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). This includes factors such as costs, productivity in terms of output rates, lead time and capacity utilisation, quality in terms of reject rates, return rates, and customer satisfaction or also KPIs such as CO2 footprint, energy efficiency and waste reduction.
Implementing generative AI in process chains makes it possible not only to make direct improvements to specific procedures, but is also able to influence broader company objectives, by optimizing relevant KPIs.
AI orchestration to optimize company processes
Automatizing complex company processes requires the integration and coordination of a range of AI systems and tools. This is known as process orchestration. It includes the management and coordination of these technologies to ensure seamless, efficient and harmonious working together. The goal is to improve the overall performance through comprehensive optimization of processes.
However, implementing AI orchestration in companies requires a carefully planned concept that also takes account of technical requirements and social objectives. One effective approach is to identify the processes to automatize, select appropriate AI and AI orchestration tools, and to develop a strategy to integrate and scale these systems appropriately. Deciding whether to use innovations such as AI-based workflows and company processes is a decision that needs to be taken carefully.
Generative artificial intelligence is already present in many companies and is becoming an important economic competition factor, which will have even greater efficiency potential in years to come. It is no longer a question of basic principles, the question is how to best use and implement AI and generative AI applications, as they change value chains and create new economic opportunities.
For the first time at EUROBIKE 2024, the Bundesverband Digitale Wirtschaft (BVDW) e.V. is curating the Mobility goes Digital Commerce conference, which is dedicated to the development of digital business models in the industry.
Learn moreKatharina Jäger

As Head of Innovation & Technology at the Bundesverband Digitale Wirtschaft (BVDW) e.V., Katharina Jäger is responsible for an area that brings together experts and visionaries as a think tank and driving force to actively shape the digital transformation. In this position, she focuses intensively on forward-looking technologies to ensure that the BVDW and its members proactively address the latest developments and trends at an early stage.

